what does ketoacidosis smell like Diabetic ketoacidosis: symptoms, causes, treatment & prevention » how
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Breakdown Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication that can occur in people who have diabetes, particularly those with type 1 diabetes. It happens when your blood sugar levels become too high, and your body starts to break down fats for energy instead of glucose. This causes the production of ketones, which can lead to a dangerous buildup in the blood. Symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis The symptoms of DKA can develop quickly and should be taken very seriously. Symptoms include: - Frequent urination - Extreme thirst - Nausea and vomiting - Abdominal pain - Confusion or difficulty concentrating - Fatigue or weakness - Dry skin and mouth - Fruity-smelling breath - Rapid breathing If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Causes of Diabetic Ketoacidosis There are several factors that can contribute to the development of DKA. One of the most common causes is not getting enough insulin. This may occur if you forget to take your insulin, if you don’t take enough, or if your insulin pump malfunctions. Other factors that can lead to DKA include: - Infection or illness - Physical or emotional trauma - Surgery or other procedures - Alcohol or drug abuse Treatment for Diabetic Ketoacidosis If you are diagnosed with DKA, you will need to be admitted to the hospital for treatment. The goal of treatment is to correct the high blood sugar levels and replace fluids and electrolytes that may have been lost. Treatment may include: - Insulin therapy to lower blood sugar levels - Fluid and electrolyte replacement, either orally or intravenously - Correction of any underlying medical conditions, such as infections or illnesses - Monitoring for complications, such as cerebral edema (swelling in the brain) Prevention of Diabetic Ketoacidosis The best way to prevent DKA is to carefully monitor your blood sugar levels and make sure you are taking your insulin as prescribed. You should also be aware of the signs and symptoms of DKA and seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of them. Other ways to prevent DKA include: - Regular inspections of your insulin pump or injection sites - Keeping emergency contact numbers on hand - Communicating with your doctor regularly about any concerns or changes in your diabetes management plan In conclusion, Diabetic Ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to life-threatening consequences. It is important to be aware of the symptoms, causes, and treatment options if you are living with diabetes. By carefully monitoring your blood sugar levels and seeking medical attention when necessary, you can help prevent the occurrence of DKA and manage your diabetes effectively.
If you are searching about Diabetic ketoacidosis: Why does my breath smell like acetone? you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Pictures about Diabetic ketoacidosis: Why does my breath smell like acetone? like What are Ketones and Why Do I Need to Test for Them? - Diabetic.org, Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Prevention » How and also Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Algorithm - Manual of Medicine. Here it is:
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Why Does My Breath Smell Like Acetone?
 www.medicalnewstoday.comacetone smell
www.medicalnewstoday.comacetone smell
What Are Ketones And Why Do I Need To Test For Them? - Diabetic.org
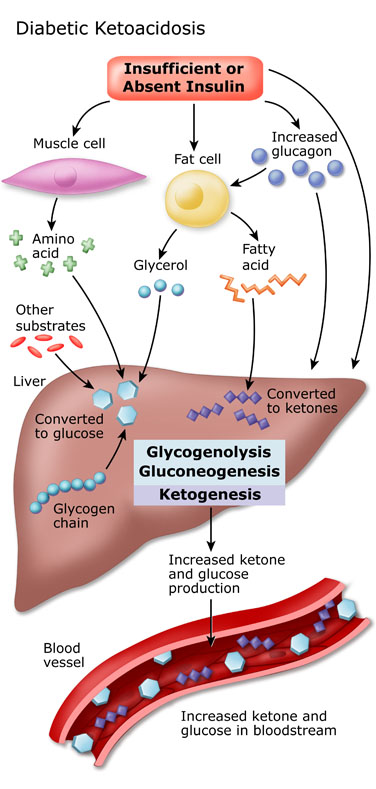
 www.diabetic.orgDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Algorithm - Manual Of Medicine
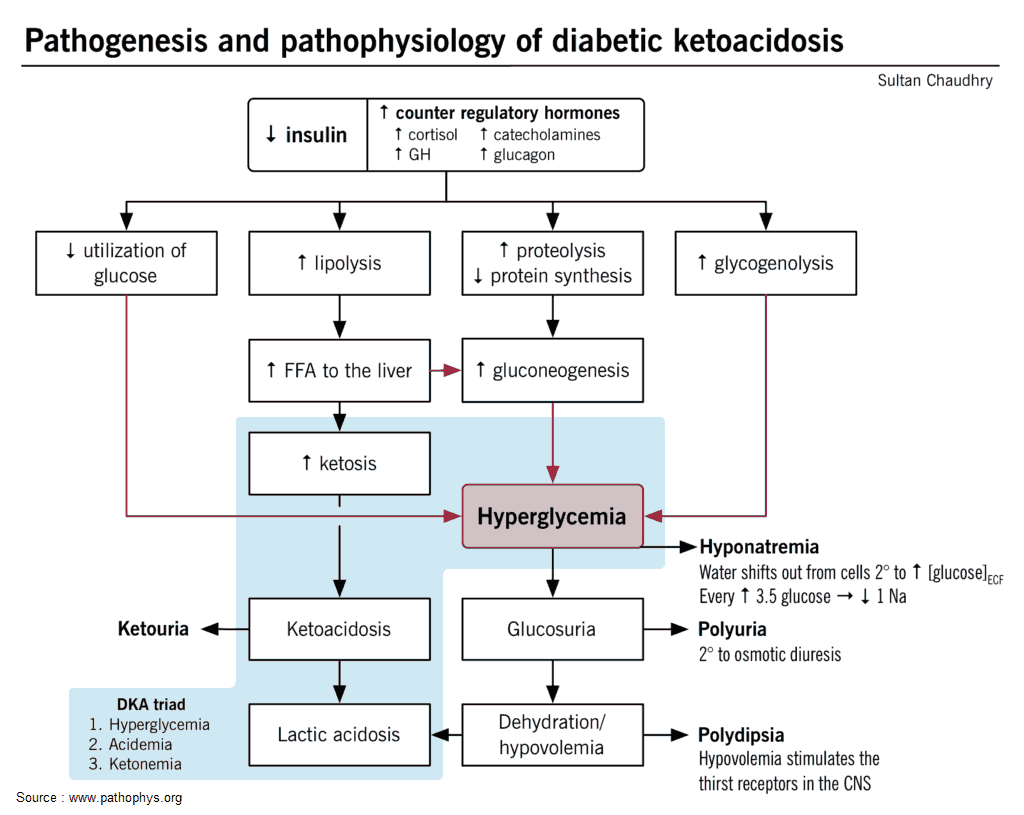 manualofmedicine.comketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology hyperglycemia hyperglycemic hyperosmolar hhs pathogenesis emergencies flowchart metabolic diabetes pathophys hyponatremia insulin acidosis
manualofmedicine.comketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology hyperglycemia hyperglycemic hyperosmolar hhs pathogenesis emergencies flowchart metabolic diabetes pathophys hyponatremia insulin acidosis
What Does Ketosis Breath Smell Like?
 www.healthnerdy.comsmell breath ketosis does
www.healthnerdy.comsmell breath ketosis does
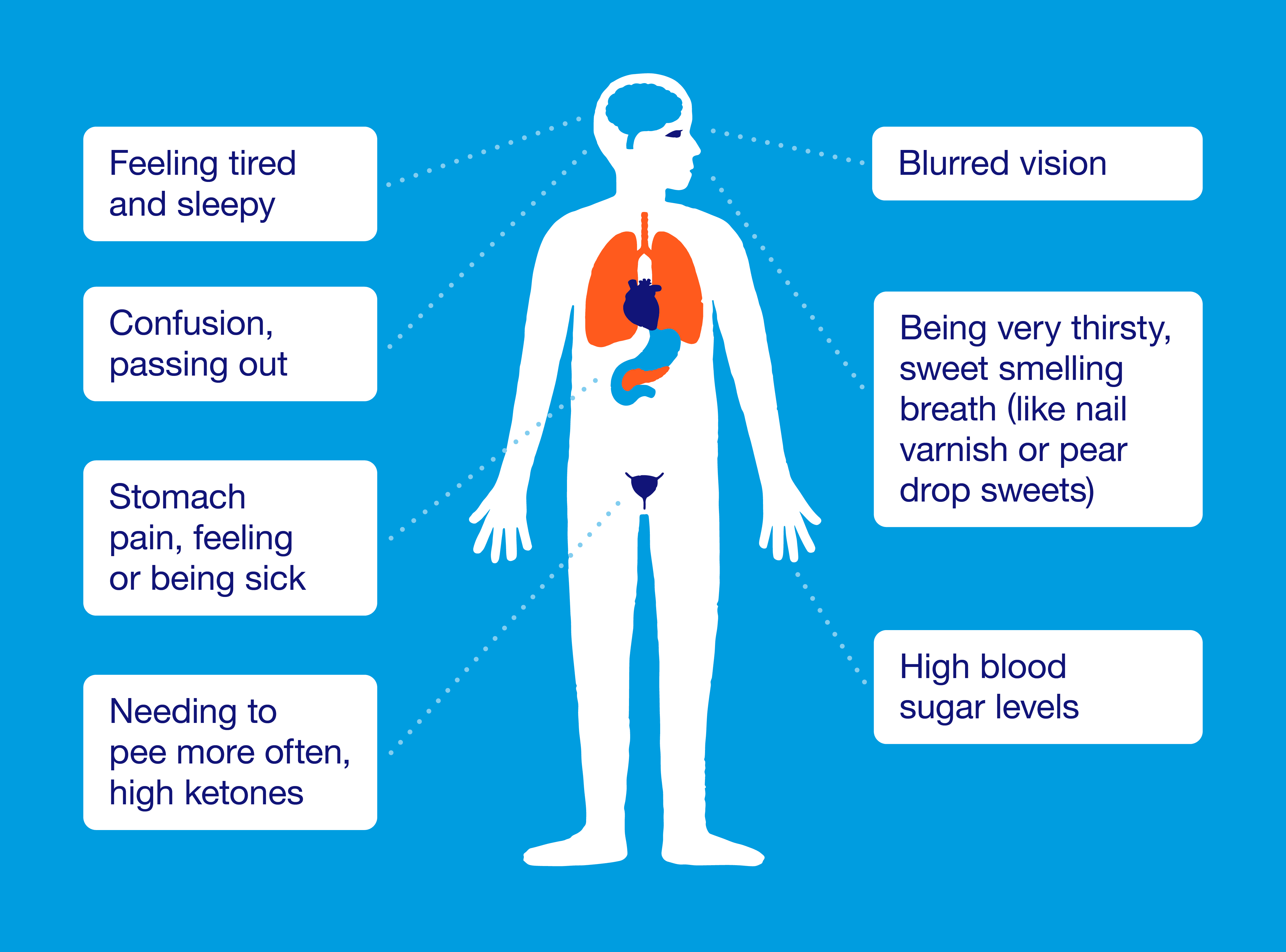
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Prevention » How
 www.howtorelief.comketoacidosis diabetes diabetic dka type causes treatment symptoms ketones prevention insulin ucsf bad complications edu breath diagram materials high glucose
www.howtorelief.comketoacidosis diabetes diabetic dka type causes treatment symptoms ketones prevention insulin ucsf bad complications edu breath diagram materials high glucose
Diabetic ketoacidosis (dka) algorithm. What are ketones and why do i need to test for them?. Ketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology hyperglycemia hyperglycemic hyperosmolar hhs pathogenesis emergencies flowchart metabolic diabetes pathophys hyponatremia insulin acidosis